How to Choose the Right Coating Machine for Battery Electrodes?
Upload Time:
Jun 26, 2025
In lithium battery production, the coating process plays a vital role in determining electrode quality. Two widely used coating methods are comma scraper coating and slot-die extrusion coating. Understanding their mechanisms, advantages, and suitable applications can help you select the optimal coating equipment for your materials and process needs.
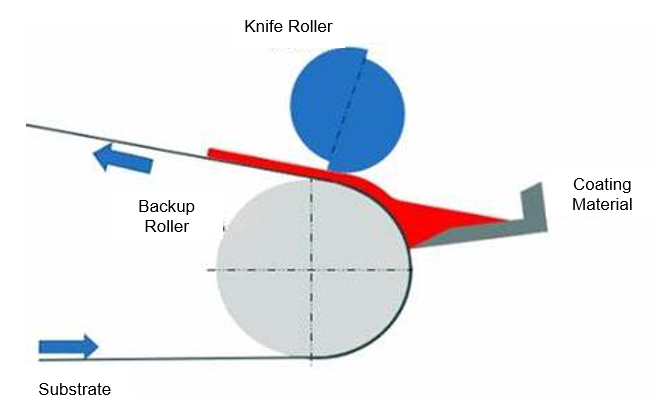
1. Comma Scraper Coating
(适用于高固含量 & 高粘度浆料 High Solid Content & High Viscosity Slurry)
In this method, the slurry directly contacts the moving substrate through a coating blade (scraper). The gap between the scraper and substrate determines the coating thickness. Excess slurry returns to the tank, and a uniform film forms on the substrate.
Key Features:
-
High coating force and precision
-
Excellent for high-viscosity and high-solid-content slurries
-
Suitable for thick coatings
-
Simple structure but requires fine blade adjustment
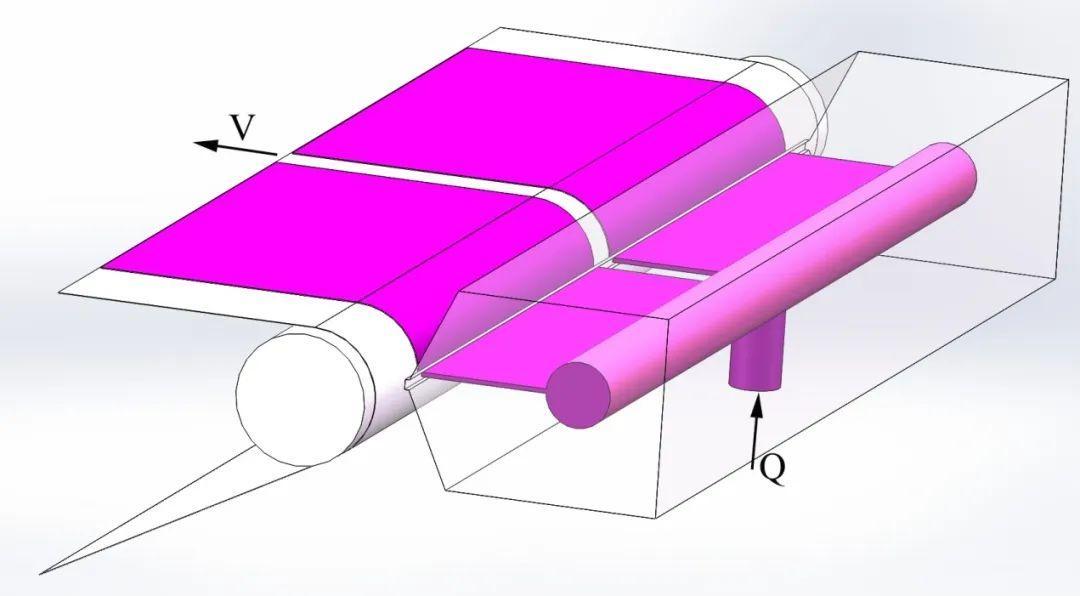
2. Slot-Die Extrusion Coating
(适用于多种浆料粘度与固含范围 Broad Material Compatibility)
This technique uses a slot-die head to extrude slurry under controlled pressure and flow rate. The slurry is dispensed through a slit, then lands evenly on the substrate via nip rollers.
Key Features:
-
Higher coating speed and precision
-
Consistent coating moisture and thickness uniformity
-
Sealed system reduces contamination risk
-
High slurry utilization rate
-
Ideal for multi-layer coatings
Which One Should You Choose?
| Criteria | Comma Scraper Coating | Slot-Die Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Slurry Viscosity | High | Wide Range |
| Solid Content | High | Medium to High |
| Coating Thickness | Thick | Adjustable |
| Uniformity | Moderate | Excellent |
| Equipment Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application Scenario | R&D, pilot-scale, specific high-solid formulas | Mass production, multi-layer systems |
Expert Tip:
For cutting-edge lithium battery or supercapacitor production, slot-die coating is increasingly favored for its precision and efficiency—especially when handling next-gen slurry systems with tight uniformity requirements.
Relevant News